Aluminium: uses and applications
Thanks to its incomparable properties, aluminium is now found in large numbers of industrial applications in the form of alloys. In plain sight or in a transparent manner, aluminium is found everywhere and plays a part in our modern lifestyle.
Numerous aluminium applications in the building industry
A metal with astonishing properties, aluminium allows many industries to innovate constantly. This is especially true in the building and public works sector, where aluminium now underpins the design of development projects particularly well suited to modern needs.
Present in numerous forms
In the building industry, aluminium is found in many products and equipment in a variety of forms:
 ■ In the form of sections: Particularly malleable, light and strong, aluminium is used in the form of sections in numerous applications, in particular for joinery, conservatories, glazed façades, glass roofs or even pergolas.
■ In the form of sections: Particularly malleable, light and strong, aluminium is used in the form of sections in numerous applications, in particular for joinery, conservatories, glazed façades, glass roofs or even pergolas.

■ In the form of roll-formed products: aluminium-rolling produces sheets or strips of aluminium that are light and strong in any dimensions. These roll-formed products are found for instance in blinds, suspended ceilings, roofing, gates or sliding partitions.

■ In solid form: robust aluminium alloys can be used to assemble all sorts of accessories used in building and public works. They can be found in guardrails, balcony structures, railings, ladders or even shelves.
So aluminium features prominently in all types of buildings and in numerous applications, even though it is preferred above all for creating lightweight and overhead structures.
Aluminium: the essential component of made-to-measure glazed solutions
Strong yet extremely light, aluminium is used to make glazed structures of all dimensions, for buildings, factories, workshops and detached houses.
In fact, there are no limits to the dimensions of a glazed surface supported by an aluminium structure. This material is used in the design of large bay windows, large conservatories or even full-height glazed façades.
Particularly strong despite its thinness, aluminium minimizes the size of structures to optimize the area of glazed surfaces. Load-bearing structures are as discreet as possible to optimize natural lighting, while offering better thermal insulation.
This slimness on large structures makes aluminium the ideal material for the design of bioclimatic structures that help make substantial energy savings.

An ideal material for renovation projects
While aluminium lends itself perfectly to modern construction projects, it has also proved its worth in the field of renovation. The properties of aluminium make it an ideal material for such work sites:
■ Its malleability adapts to all types of existing structures, with precise adjustments and without any alterations to existing brickwork.
■ The possibility of creating small or very large made-to-measure sections and frames means it can be adapted to meet all requirements.
■ Machined to order, and with the option of being solid-tinted and textured, aluminium adapts to all architectural styles, even the most traditional ones
Aluminium sections can be used to renovate a house in its original style while benefiting from the advantages of aluminium in terms of comfort, safety and energy efficiency.
Aluminium, a revolution for the transport industry
Much lighter than steel, while offering excellent resistance to corrosion and stress, aluminium has played a predominant role in the transport industry from the time of its industrialization.
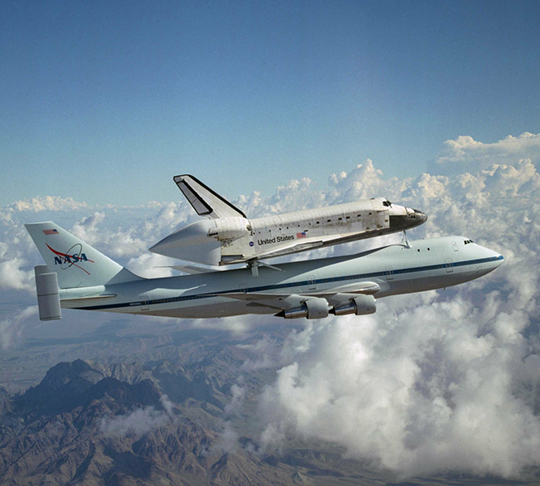
Lighter for aircraft and spacecraft
For civil and military aircraft, as for space launchers and spacecraft, too heavy a structure penalizes the payload and fuel load. Eliminating surplus kilos has always been a key priority of the sector since the very beginnings of aviation.
Offering very high mechanical strength for a very restricted weight, aluminium is used to design lighter flying machines or satellites while remaining very sturdy and remarkably durable over time.
Albeit in competition with carbon fibre composites, aluminium today is still the reference material for the aeronautical and aerospace industry.

Growing importance in the automotive industry
Closer to our daily uses, aluminium is also helping make steady improvements in the automotive industry. The proportion of aluminium in land vehicles has constantly increased over the years, endowing them with numerous advantages:

Lighter to reduce fuel consumption

Better road-holding and fewer accidents
Easier recycling of vehicles
Ships and trains: towards high speed
Aluminium has been used in the shipbuilding and rail industries since the end of the 19th century to reduce the weight of vehicles, lower their centre of gravity and thereby improve their performance for the same mechanical strength.
Weight reduction combined with better motorization has enabled the development of high-speed trains and ships that can carry large numbers of passengers. Aluminium is thus integral to the performance of high-speed trains or rapid ferries.

Diverse uses, from our everyday domestic lives to the most demanding industries
Corrosion-resistant, impermeable to air, water, ultraviolet and microorganisms, electrically conductive and particularly strong, aluminium is an ideal product for a multitude of uses. The truth of the matter is that it is found literally everywhere in our everyday life and in cutting-edge industries.
In food processing and packaging
Our most common and conscious contact with aluminium is in our kitchens. In addition to aluminium foil, this material is found in:
- Food-grade containers,
- Cardboard cartons,
- Drink cans,
- Coffee capsules,
- Jar lids.
It is obviously omnipresent in the kitchen, both in utensils and in saucepans or household appliances.
Ideal for packaging, aluminium is used in many fields unrelated to food: sprays, paint, pharmaceutical products, etc.

Did you know?
Aluminium is the second most-used metal on earth, after steel. However, it is much easier to recycle, without impairing its quality or properties.
Power transmission, everyday items and other uses
A better electrical conductor than copper, aluminium is slowly but surely becoming a reference for high-voltage line equipment, transformer windings or underground and submarine cables. As it is also lighter and stronger than conventional materials, aluminium could impose itself as the new standard in the electrical or even electronic industry.
On a day-to-day basis, aluminium is a light and strong metal, but also relatively inexpensive, used to design affordable products for everyone. Unwrought, rolled or extruded, it is found in computer or telephone casings, bicycle frames, bolts and screws, decorative items, home furnishings or camping equipment.

